Oracle Autonomous Database Tools
Author: Donatien MBADI OUM, Oracle Consultant
1.
Introduction
In this section, we are going to show
you an overview of REST APIs and OCI Command Line Interface. We are also going
to talk about various tools like SQL Worksheet, Data Modeler, Oracle
Application Express (APEX), Oracle Machine Learning- (OML) and others.
2.
Using REST APIs
REST stands for Representational State
Transfer. It’s a software architectural style that describes uniform interface
between physically separate components, often across the Internet in a
client-server architecture.
Oracle’s Cloud offers full REST APIs
for Database Administrators and Developers who would prefer to interact with a
Cloud programmatically, as opposed to going through the Cloud Console. This
provides the mechanism for developing customized deployment and management
scripts that can be saved and reused for deployments.
OCI APIs are typical REST APIs that
use HTTPS requests and responses and support HTTPS and SSL protocol TLS1.2, the
most secure industry standards. Calls to the OCI using REST APIs can be written
in popular scripting languages such as node.js, Python, Ruby, Perl, Java, c#,
bash or curl.
All OCI API requests must signed for
authentication purposes. The steps to create and sign API requests are:
-
Form the HTTPS request (SSL protocol TLS 1.2 is required)
-
Create the signing string, which is based on parts of the
request
-
Create the signature from the signing string, using your
private key and the RSA-SHA256 algorithm
-
Add the resulting signature and other required information to
the authorization header in the request
-
You will also need to generate an SSH key pair in the pem
format
Example 1: Creates a new Autonomous Database in the
Phoenix data center, with a database name adatabasedb1, the specified password, 8 CPUs and 1TB of
storage.
POST /20160918/autonomousDatabases
Host: database.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com
<authorization and other headers>
{
"compartmentId" :
"ocid.compartment.oc1..<unique_ID>",
"displayName" :
"example_autonomous_database",
"dbName" :
"adatabasedb1",
"adminPassword" :
"<password>",
"cpuCoreCount" : 8,
"dataStorageSizeInTBs" : 1
}
Example 2: Gets the details of the
specified ADB:
GET
/20160918/autonomousDatabases/<autonomousDatabaseId>
Host:
database.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com
<authorization
and other headers>
Example 3: Start and Stop a specified
ADB
POST
/20160918/autonomousDatabases/<autonomousDatabaseId>/actions/start
Host:
database.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com
<authorization
and other headers>
POST
/20160918/autonomousDatabases/<autonomousDatabaseId>/actions/stop
Host:
database.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com
<authorization
and other headers>
Example 4: Update one or more
attributes of the specified ADB
PUT
/latest/autonomousDatabases/<autonomousDatabaseId>
Host:
database.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com
<authorization
and other headers>
{
"cpuCoreCount" : 20
}
Example 5: Delete the specified ADB
DELETE
/20160918/autonomousDatabases/<autonomousDatabaseId>
Host:
database.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com
<authorization
and other headers>
3.
Using OCI CLI
CLI stands for Command-Line Interface.
The CLI is a small lightweight tool that you can use either on its own or in
conjunction with the console, to complete OCI tasks. The CLI provides the same
core functionality as the console, plus additional commands. You can also use
CLI to run scripts.
The CLI is built on Python and it can
be run on Mac, Windows or Linux. The Python code makes call to the OCI APIs to
provide the functionality that is implemented within our various Cloud.
To install and use the CLI, you must
have:
-
An OCI account
-
A user created in that account, in a group with a policy that
grants the desired permissions
-
A keypair used for signing API requests, with the public key
uploaded to Oracle. Only the user calling the API should possess the private
key
-
Python version 2.75, 3.5 or later, running on Mac, Windows or
Linux. Note that if you use the OCI Installer and do not have Python on your
machine, the Installer automatically install a proper version of Python for
you.
The supported ADB commands that you
can invoke using the OCI CLI are:
change-compartment Move the Autonomous Database...
configure-key Configures the Autonomous...
create Creates a new
Autonomous...
create-adb-cross-region-data-guard-details
Details to
create an...
create-from-backup-id Creates a new Autonomous...
create-from-backup-timestamp Creates a new Autonomous...
create-from-clone Creates a new Autonomous...
create-refreshable-clone Creates a new Autonomous...
data-safe The Data Safe to use
with this...
delete Deletes the
specified...
disable-autonomous-database-management
Disables
Database Management...
disable-operations-insights Disables Operations Insights...
enable-autonomous-database-management
Enables
Database Management...
enable-operations-insights Enables the specified...
fail-over Initiates a failover
the...
generate-wallet Creates and downloads a
wallet...
get Gets the details
of the...
list Gets a list of Autonomous...
list-clones Lists the Autonomous
Database...
manual-refresh Initiates a data refresh
for...
restart Restarts the
specified...
restore Restores an Autonomous...
rotate-key Rotate existing...
shrink This operation
shrinks the...
start Starts the
specified...
stop Stops the specified
Autonomous...
switchover Initiates a switchover of
the...
update Updates one or more
attributes...
This example creates an ADW:
COMPARTMENT_ID="ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaaaaaaanttqtoswfsyt6kr72rhoezawt4dilortr3gix3om4iyxlcxclc2a"
oci db
autonomous-database create -c $COMPARTMENT_ID \
--db-name
"ociadwprd" \
--display-name
"OCIADWPROD" \
--admin-password
"Collovaty_4321#" \
--cpu-core-count
"1" \
--data-storage-size-in-tbs
"1" \
--db-workload
"OLTP" \
--license-model
"BRING_YOUR_OWN_LICENSE" \
--is-auto-scaling-enabled
"FALSE" \
4.
Autonomous Database tools
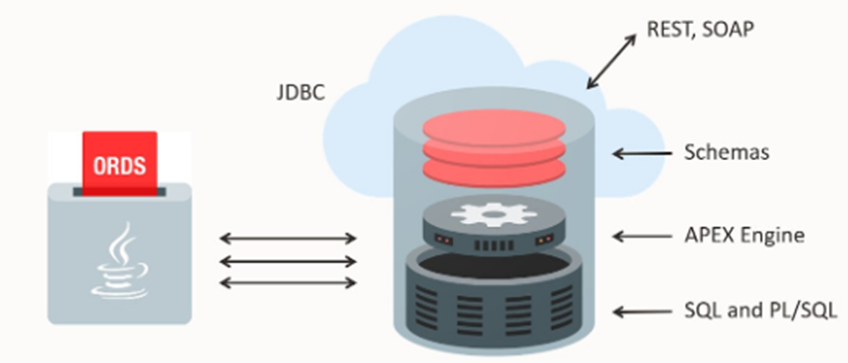
ADB comes with a suite of development tools
pre-deployed with nothing new to buy and nothing new to install. These are
web-based applications that used Oracle REST data service to provide many of
database development and administration features. These suite of tools can
accessed directly from the ADB page of the OCI console.
After selecting your ADB instance, click on Database
Actions button.
Connect to your ADB using an authenticated user.
This brings you to the Database Actions main page.
4.1. SQL Worksheet
It
enables you to enter and execute SQL and PL/SQL statements, creates database
objects and save data into a file. Some other features are syntax highlighting
and error detection. Use the left pane to for navigating worksheets and
objects, the editor for executing SQL statements and the output pane for
viewing the results.
4.2. Data Modeler
The Data Modeler tool provides an integrated version of Oracle SQL
Developer Data Modeler with basic reporting features.
You can create diagram for from
existing schemas, retrieve data dictionary information, generate Data
Definition Language (DDL) statements and export diagram.
Use the left pane for navigating
objects and diagrams, the Editor for working with relational diagrams and the
right pane for viewing the properties of the selected object.
4.3. APEX
Oracle Application Express (APEX) is a low-code development platform that
enable you to build scalable, secure enterprise applications with word class
features that can be deployed anywhere. APEX is a fully-supported feature of
Oracle Database. If you have Oracle database, you already have APEX.
Oracle takes care of configuration, tuning, backup, patching, encryption,
scaling and more and leaving you free to focus on solving your business
problem. You will to be log as administrator at first. Than you may create
workspaces for your respective users and log in with those associated credentials.
APEX provides you an easy-to-use
browser-based environment to load data, manage database objects, develop REST
interfaces and build applications which look and run great on both desktop and
mobile devices.
There are no limit of developers or
end users for your applications. Anything you can express with SQL can be
easily employed in an APEX application. Instead of writing code by hand, you
are able to use intelligent wizards to guide you through the rapid creation of
applications and components.
4.4. Oracle Machine Learning
Oracle Machine Learning (OML) is enabled on ADB. The three
predominant features of OML are:
-
AutoML: Automation of algorithm selection, feature select and
automatic model tuning
-
OML4Py: Machine Learning in Oracle database accessible via Python
and R
-
Data Insights: Automatically discover hidden patterns,
anomalies and outliers.
A new capability has been introduced
with Oracle Machine Learning called Automatic Machine Learning or AutoML. Its
goal is to increase data scientist productivity while reducing overall compute
time. In addition, AutoML enables non-expert users to leverage Machine Learning
by not requiring deep understanding of the algorithms and their understanding.
AutoML consists of three main
functions:
-
Auto Algorithm Selection: the goal is to identify the
in-database algorithms that are likely to achieve the highest model quality
-
Auto Feature Selection: the goal is to de-noise data by
eliminating features that not add value to the model.
-
Auto Model Tuning: the goal is to tune algorithm hyper
parameters, those parameters that determine the behavior of the algorithm on
the provided data.
Oracle Machine Learning for Python
(OML4Py) is a component of Oracle Autonomous Database, which includes Oracle
Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW), Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing
(ATP), and Oracle Autonomous JSON Database (AJD). By using Oracle Machine
Learning Notebooks on Oracle Autonomous Database, you can run Python functions
on database data for exploration, preparation, and modeling while leveraging
Oracle Database as a high-performance computing environment.
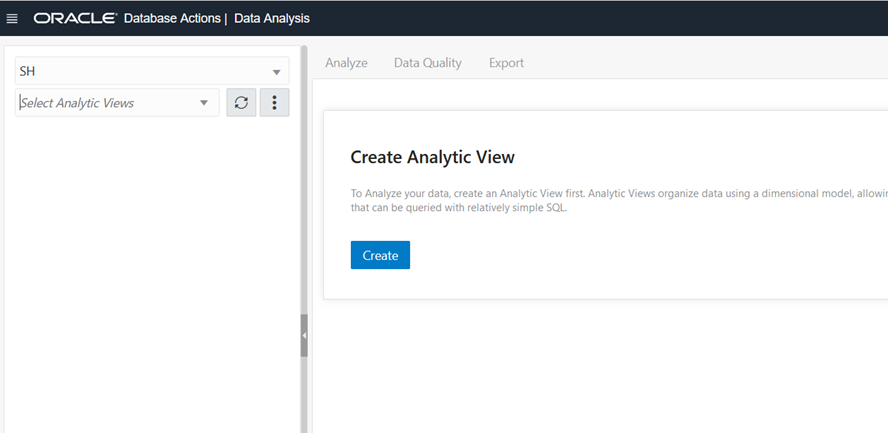
4.5. Data Analysis
The data analysis tools enables you to
create analytics views with multidimensional metadata. You creates analytic
views on top table with several dimensions and hierarchies. Analytic views
refer to tables in database and allow users to create hierarchies and
dimensions.
With Data Analysis tool you can:
-
Visualize,
analyze and inspect your data clearly and efficiently with pivot tables
-
Calculate
total number of errors present in the Analytic View you create and provide
solutions to minimize the errors
-
Automatically
display meaningful insights to help you make better decisions
-
Analyze
your data across dimensions with support for hierarchical aggregation and
drill-down
-
Share
your Analytic Views with the tool of your choice over various options of raw
data consumption to draw meaningful insights and make them accessible to any
user
4.6. Data Load and Data Transform
You
can load data into your ADB from a local file system on a remote database or
from an object store in the cloud somewhere using Data Load tool. You can also
link to your data in on-premises and cloud storage sources (Oracle, Amazon S3
and Azure), so that changes in the sources are reflected automatically. The
supported data formats are CSV, AVRO, PARQUET, JSON, ORC or Delimited TXT. You
can also create a feed from your cloud storage sources, so that when new data
appears, it’s loaded automatically.
|
Operation |
Source Location |
Description |
|
Load data |
Local file Database Cloud storage |
Load data from files on your local device, from remote databases, or from
cloud storage into tables in your Oracle Autonomous Database. |
|
Link data |
Database Cloud storage |
Create external tables or views in your Oracle Autonomous Database that
link to data in cloud storage or remote databases. Changes to the source data
automatically appear in the target objects. |
|
Feed data |
Cloud storage |
Set up a feed of data from a cloud storage bucket into a table. Changes
to the source data load into the target table as scheduled or on demand. |
Data
transform is new and easy-to-use web user interface based on Oracle Data
Integrator (ODI). It consists of simple drag-and-drop data for transformations.
Auto code is generated automatically for all ODI and sources and targets.
4.7. Business Model
Data Analysts typically don’t work
directly against tables in a database. Data Analysts work with a semantic
model. This is a layer above the physical data structure. All business model
are not created equal. Most popular self-service analytic tools define the business
the business in the tool itself. A common problem with this is that different
analysts each with their own self-service tool can easily define different and
contradictory business model every on the same data sets.
Oracle approach is to push the business
model into the database layer. There is only need to be defined once, which in
itself is a great productivity boost. Most importantly, this promotes
consistency. By sharing the common business model, all analysts get a
consistent view of the business.
A further advantage of defining
business models in the database is performance. A key insight is that business
analysts typically access data at the top level. By automatically recognizing
the hierarchy and defining it in the database, ADB can automatically compute
and store these top-level aggregates. Oracle calls this materialization of
aggregate caches.
4.8. Data Insights
As
you know, RDBMS already have many machine learning algorithms built-in and the
analytic view is what allow RDBMS to understand the user’s intended use of the
data in the database.
Automatic
insights discovery:
-
Crawls over business model running as background process
-
Discovers hidden patterns, anomalies and outliers
-
Variety algorithms including regression slope
Usage:
-
Drill down on a specific insight
-
Significant deviations between predicted and actual values
highlighted
4.9. Data Catalog
The catalog has a health of
information about we have been working with. It helps to understand data
dependencies and the impact of changes.
OCI Data Catalog is a metadata
management service that helps data professionals discover data and support data
governance in Oracle ecosystem. It’s also a data asset inventory with business
context and a unified metastore for the lakehouse and it’s free with OCI.





















Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire